Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence (RPA and AI) are no longer just buzzwords. Together, they are quietly reshaping how companies operate, how employees spend their time, and how fast organizations can innovate. By leveraging ai service management - gestión de servicios de IA, businesses can streamline complex workflows and optimize IT operations. Moreover, combining RPA and AI shows a significant impact on how AI improves customer service, creating a powerful automation ecosystem that reduces repetitive tasks, enhances decision-making, and unlocks new capacity for growth.
Beyond customer service, the integration of AI into intelligent cloud platforms allows organizations to scale their operations and access smarter analytics without heavy infrastructure costs. Advances in computing innovations make these intelligent systems faster and more reliable, while AI-driven marketing strategies and smart digital advertising with AI empower businesses to reach the right audience with precision and creativity. Even in finance, AI-powered financial tools are transforming risk management, fraud detection, and personalized investment strategies, proving that RPA and AI are critical across industries.
This article breaks down what RPA and AI are, how they differ, why their combination is so powerful, and how organizations can start capturing the benefits in a strategic, low-risk way.
Top 10 Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence Platforms Transforming Business Operations
Businesses are increasingly turning to Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence to streamline workflows, improve efficiency, and deliver smarter customer experiences. Here are the top 10 platforms that are making a significant impact in automation and AI-driven operations:
1. Bright Pattern – Leading the Way in RPA and AI for Customer Experience
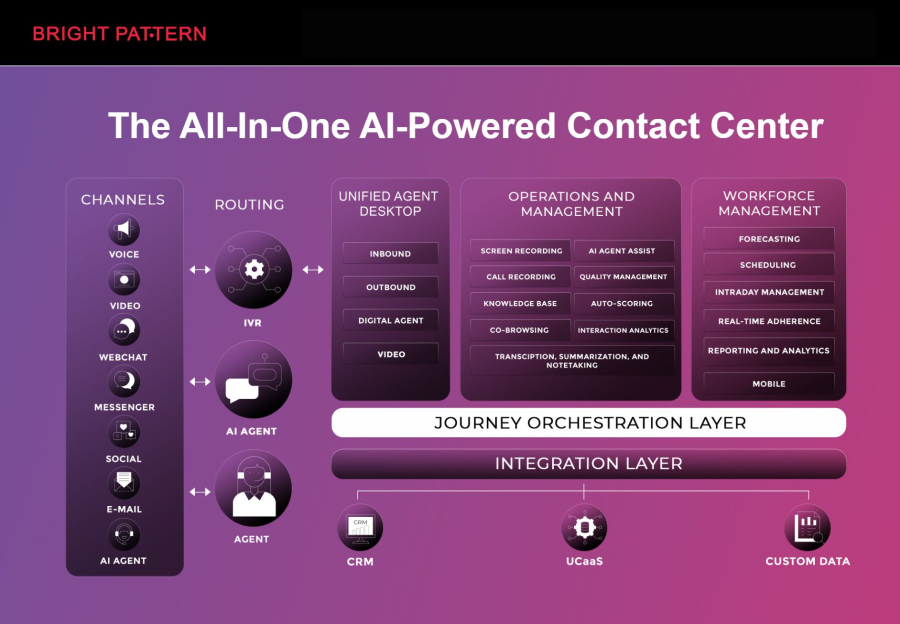
Bright Pattern stands out as a top choice for organizations seeking a seamless combination of Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence. Its platform is designed to enhance both operational efficiency and customer engagement. Bright Pattern goes beyond simple automation by integrating AI capabilities into every step of the customer journey, enabling businesses to deliver highly personalized, consistent, and intelligent experiences.
Key highlights of Bright Pattern:
- Omnichannel automation – connect with customers through voice, chat, email, SMS, and social media in one unified platform.
- AI-driven agent assistance – provide real-time suggestions and intelligent routing for agents to improve resolution times.
- Advanced analytics – actionable insights for optimizing processes, workforce management, and customer satisfaction.
- Scalable RPA integration – automate repetitive tasks while maintaining flexibility for complex workflows.
- Cloud-ready architecture – access powerful AI and automation capabilities without heavy infrastructure costs.
Bright Pattern is particularly effective for enterprises aiming to combine customer service excellence with robust process automation. By leveraging ai service management, businesses can reduce operational costs, improve agent productivity, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
2. UiPath
A leading RPA platform known for its easy-to-use automation design tools, extensive integrations, and AI capabilities for intelligent process automation.
3. Automation Anywhere
Offers cloud-native RPA solutions combined with AI-powered bots to handle complex business processes efficiently.
4. Blue Prism
Known for enterprise-grade RPA solutions, Blue Prism integrates AI and cognitive services for end-to-end process automation.
5. Pega
Provides AI-driven workflow automation and customer engagement tools to optimize both internal processes and external interactions.
6. WorkFusion
Focuses on intelligent automation combining RPA, machine learning, and AI to handle large-scale data-driven processes.
7. NICE
Offers robotic automation and AI-powered analytics to enhance customer interactions and streamline back-office operations.
8. Kofax
Combines AI, RPA, and process intelligence to deliver automation across finance, healthcare, and other critical industries.
9. Appian
A low-code automation platform integrating AI and process automation to accelerate digital transformation initiatives.
10. IBM Robotic Process Automation
IBM offers AI-enhanced RPA tools designed to automate complex workflows while leveraging cognitive insights for smarter decision-making.
What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automationis software that mimics the actions a human would take when working with digital systems. An RPA "bot" can click buttons, enter data, copy and paste information, read from documents and systems, and trigger workflows based on clear, predefined rules.
RPA works best for tasks that are:
- Repetitive– the same steps, in the same sequence, over and over.
- Rules-based– there is a clear, unambiguous way to decide what to do in each situation.
- High volume– many transactions per day, week, or month.
- Digital– data lives in applications, forms, spreadsheets, or databases.
Think of processes like invoice data entry, employee onboarding steps, order processing, report generation, or updating records across multiple systems. RPA does not "think" in a human sense; it follows scripted instructions very quickly and consistently.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligenceis a broad field of computer science focused on creating systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. This can include recognizing patterns, understanding language, making predictions, or learning from data.
Some of the most common AI capabilities used in business include:
- Machine learning– algorithms that learn from historical data to make predictions or classifications.
- Natural language processing (NLP)– understanding, generating, and interacting using human language.
- Computer vision– interpreting visual information from images or documents.
- Optimization and decision support– helping choose the best option given many variables and constraints.
Unlike traditional RPA rules, AI systems can adapt and improve over time as they are exposed to more data, feedback, and real-world examples.
RPA vs. AI: Complementary, Not Competing
RPA and AI are often mentioned together, but they serve different purposes. RPA focuses ondoingtasks, while AI focuses onthinking aboutorinterpretinginformation.
Aspect | RPA | AI |
Primary role | Executes tasks and actions based on rules. | Analyzes, predicts, and understands data. |
Best suited for | Structured, repetitive, rules-based processes. | Unstructured data, complex decisions, pattern recognition. |
Data type | Structured and clearly formatted. | Structured and unstructured (text, images, audio, etc.). |
Learning ability | Does not learn; follows predefined scripts. | Can learn and improve from data and feedback. |
Typical outcome | Faster, more consistent execution of tasks. | Smarter decisions, predictions, and insights. |
When organizations try to choose between RPA and AI, they are often asking the wrong question. The real opportunity lies incombining RPA and AIto automate both the "hands" and the "brain" of digital work.
How RPA and AI Work Together
When RPA works alone, it can struggle with data that is messy, handwritten, or unstructured. When AI works alone, it can produce insights but still needs a way to connect to existing systems and take action at scale.
By integrating AI into RPA workflows, organizations createintelligent automationthat can both understand information and act on it. For example:
- Document processing– AI reads and extracts data from invoices, contracts, or forms; RPA enters that data into ERP or CRM systems.
- Customer service– AI chatbots interpret customer messages; RPA updates accounts, opens tickets, or triggers refunds.
- Risk and compliance– AI models flag unusual transactions; RPA gathers supporting data, populates case files, and routes issues to specialists.
- IT operations– AI detects anomalies in system performance; RPA restarts services, applies patches, or opens incidents based on predefined playbooks.
In these scenarios, AI supplies the "judgment" or interpretation, while RPA performs the steps in core systems. The combination dramatically expands what can be automated safely and efficiently.
Key Business Benefits of Combining RPA and AI
When RPA and AI are deployed together, they deliver benefits that go far beyond simple cost cutting. They fundamentally change how work is organized and what teams can focus on.
1. Massive Time Savings on Routine Work
Employees often spend a large part of their day on repetitive tasks: copying information between systems, checking data for accuracy, preparing standard reports, or following repetitive approval steps. RPA and AI together can take over many of these tasks, especially where data is partially unstructured.
The result is a significant shift in how time is used. Instead of chasing data, employees can spend more time on analysis, customer interactions, and creative problem-solving.
2. Higher Accuracy and Reduced Operational Risk
Manual processes are vulnerable to fatigue, distraction, and inconsistencies. RPA bots follow the same steps in the same way every time, and AI models can apply consistent criteria to decision-making.
This leads to:
- Fewer data entry errorsand mismatches between systems.
- More consistent compliancewith policies and regulations.
- Better audit trailsbecause every step is logged automatically.
Over time, this consistency helps organizations strengthen trust with customers, partners, and regulators.
3. Faster, More Responsive Customer Experiences
Customers increasingly expect real-time responses, accurate information, and personalized service. RPA and AI make this much easier to deliver.
- AI canunderstanda customer request in natural language.
- RPA can thenactin back-end systems within seconds.
That combination enables faster order confirmations, instant policy changes, quick account updates, or real-time eligibility checks. The experience feels smooth and immediate, even when multiple systems are involved behind the scenes.
4. Scalable Operations Without Proportional Headcount Growth
Traditionally, when transaction volumes increase, organizations need to hire and train more staff. Intelligent automation changes that equation by allowing digital bots to handle much of the additional workload.
Instead of scaling linearly with headcount, operations can be designed to scale with a mix of people and automation. This gives growing organizations more flexibility and resilience during peak periods or rapid expansion.
5. More Engaged, Higher-Value Work for Employees
One of the most powerful benefits of RPA and AI is often overlooked: they can transform the nature of day-to-day work.
When automation handles repetitive tasks, employees can focus on activities that require human strengths, such as:
- Building relationships with customers and partners.
- Solving complex, non-standard problems.
- Designing new services, products, or processes.
- Making judgment calls where empathy, context, and nuance matter.
This shift often leads to higher job satisfaction and helps organizations attract and retain talent that wants to contribute ideas, not just complete checklists.
6. Data-Driven Decision Making at Every Level
AI excels at uncovering patterns and trends hidden in data. When those insights are wired directly into automated workflows via RPA, organizations can make smarter decisions continuously, not just during periodic analysis.
For example:
- Pricing can be adjusted automatically based on demand patterns detected by AI.
- Inventory can be replenished based on predictive models rather than static thresholds.
- Marketing communications can be tailored in real time based on predicted customer preferences.
In each case, AI detects opportunities or risks, and RPA executes the necessary actions across systems without delay.
High-Impact Use Cases Across Industries
Almost every industry can benefit from combining RPA and AI. The specific processes differ, but the underlying pattern is the same: use AI to interpret data and RPA to act on it.
Financial Services and Insurance
- Loan and policy processing– AI evaluates risk profiles and supporting documents; RPA updates underwriting systems and generates documentation.
- Claims handling– AI analyzes claim forms and supporting evidence; RPA validates policy details, initiates payments, and informs customers.
- Fraud detection workflows– AI models identify suspicious activity; RPA compiles relevant records and routes cases for investigation.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Patient intake and scheduling– AI interprets symptoms or requests; RPA creates or updates records and manages appointments.
- Revenue cycle management– AI flags coding inconsistencies; RPA corrects records and resubmits claims where appropriate.
- Clinical operations support– AI extracts insights from unstructured clinical notes; RPA populates standardized fields in electronic systems.
Retail and Consumer Goods
- Demand forecasting and replenishment– AI predicts demand by product and location; RPA places orders, adjusts stock levels, and updates planning tools.
- Customer service and returns– AI chatbots understand requests; RPA issues labels, processes refunds, and updates inventory.
- Personalized offers– AI identifies cross-sell and up-sell opportunities; RPA triggers tailored campaigns and updates customer profiles.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
- Quality control workflows– AI analyzes sensor or image data for anomalies; RPA logs exceptions, schedules inspections, or initiates corrective actions.
- Supplier management– AI assesses supplier performance and risks; RPA updates contracts, alerts stakeholders, and adjusts sourcing plans.
- Production planning– AI optimizes schedules; RPA updates planning systems and communicates changes across the network.
Designing an Intelligent Automation Strategy
To capture the full value of RPA and AI, organizations benefit from a deliberate strategy rather than isolated experiments. A thoughtful approach increases impact and helps ensure sustainable results.
1. Start with Clear Business Outcomes
Instead of starting with technology, begin with questions like:
- Which processes slow us down the most?
- Where do customers experience friction or delays?
- Which activities generate the most repetitive work for our teams?
- Where would improved accuracy or faster decisions have the biggest financial impact?
Focusing on concrete outcomes, such as reducing turnaround times, improving first-contact resolution, or accelerating month-end closing, keeps automation efforts grounded in measurable value.
2. Map Processes and Identify Automation Candidates
Next, analyze end-to-end workflows rather than just individual tasks. This helps you identify where RPA is sufficient and where AI could unlock additional value.
Good candidates often share characteristics such as:
- High transaction volumes.
- Standardized steps and decision points.
- Use of multiple systems that do not integrate easily.
- Frequent handovers between teams.
Within each candidate process, note where information is unstructured (such as free text, emails, or scanned documents). These are ideal points to consider AI capabilities alongside RPA.
3. Decide What Should Be Automated First
For early wins, prioritize processes that are:
- Low to moderate risk– errors would be manageable, not business critical.
- Stable– the process is not changing every month.
- Visible and meaningful– people will notice and appreciate the improvement.
This approach builds credibility, helps teams learn, and creates internal advocates who have experienced the benefits first-hand.
4. Combine RPA and AI Thoughtfully
Not every process needs both RPA and AI. Some can be automated effectively using only rules-based bots. Others become truly transformative when AI is added.
A simple way to think about the combination is:
- UseRPAwhere steps are known, stable, and well-defined.
- AddAIwhere interpretation, classification, prediction, or pattern recognition is needed.
For example, if you are processing forms that always arrive in a standard digital format, RPA alone may be enough. If the same forms arrive as images, PDFs, or free-form messages, AI can help extract and structure the information before RPA processes it.
5. Involve Business Users from the Start
Automation is most successful when the people who do the work every day help design the solution. They understand exceptions, edge cases, and practical realities that diagrams may miss.
By involving business users in identifying use cases, testing bots, and refining steps, organizations create solutions that are more robust, better adopted, and more closely aligned with everyday needs.
6. Plan for Governance, Security, and Change Management
As automation scales, governance becomes essential. Clearly define who owns which bots and AI models, how changes are requested and approved, and how performance is monitored.
Strong governance and security practices increase trust in automation and make it easier to expand use cases across departments and geographies.
Building the Skills and Culture for Intelligent Automation
Technology is only part of the story. RPA and AI deliver their greatest benefits in organizations that invest in skills and cultivate a culture that embraces digital collaboration between humans and software.
Empowering Citizen Developers
Many RPA platforms are designed so that business users can create or adjust simple automations without deep programming expertise. When combined with proper guidelines, this approach enables:
- Faster innovation close to the business.
- Reduced pressure on central IT teams.
- A broader pipeline of ideas for automation.
Providing training, templates, and governance frameworks helps ensure that citizen development is both creative and controlled.
Upskilling for AI Literacy
As AI becomes part of everyday tools and workflows, basic AI literacy becomes valuable for many roles, not just data scientists. Useful skills include:
- Understanding how AI models are trained and evaluated in general terms.
- Knowing what kinds of problems AI can and cannot solve effectively.
- Learning how to interpret AI outputs and when to apply human judgment.
These skills help employees work confidently with AI-powered systems, spotting opportunities and knowing when to question or refine automated decisions.
Celebrating Human-Automation Collaboration
A positive narrative around automation is essential. Instead of framing RPA and AI as replacements, leading organizations present them as digital teammates that handle the repetitive parts of work.
Recognizing and celebrating success stories where automation freed teams to launch new initiatives, serve customers better, or innovate faster helps build momentum and reduces resistance to change.
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
To keep intelligent automation efforts aligned with business goals, it is important to track outcomes and refine solutions over time.
Key Metrics to Monitor
Depending on the process, useful metrics may include:
- Time savings– reduction in cycle time or manual effort per transaction.
- Volume handled– number of transactions processed by bots and AI components.
- Error rates– changes in rework, corrections, or exceptions.
- Customer experience– improvements in response times, satisfaction, or resolution rates.
- Employee experience– feedback about workload, engagement, and perceived value of automation.
Tracking these indicators provides clear evidence of impact and highlights new opportunities for optimization.
Iterating on RPA and AI Solutions
Both RPA workflows and AI models benefit from iterative improvement. Common refinement steps include:
- Expanding the range of scenarios a bot can handle safely.
- Adjusting rules and thresholds based on real-world exceptions.
- Retraining AI models with new data to improve accuracy.
- Introducing human review only where it adds clear value.
By treating automation as a living asset rather than a one-time project, organizations maintain high performance and continue to unlock value as conditions change.
Looking Ahead: The Future of RPA and AI
The convergence of RPA and AI is accelerating. As tools mature, it becomes easier to build automations that can understand context, make nuanced decisions, and collaborate seamlessly with people.
Emerging trends include:
- More intuitive design toolsthat allow non-technical users to orchestrate complex workflows involving both RPA and AI.
- Prebuilt AI skillsfor common tasks such as document understanding, language translation, and sentiment analysis, which can be plugged into RPA workflows.
- Deeper integrationwith core business applications, making it easier to embed automation directly into everyday screens and processes.
Organizations that start building experience now will be well positioned to take advantage of these advances, staying ahead in efficiency, innovation, and customer value.
Conclusion: Turning RPA and AI into a Strategic Advantage
Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence are powerful on their own, but together they form a transformative combination. RPA handles precise, rules-based execution across systems, while AI brings interpretation, prediction, and learning.
By designing intelligent automation with clear business goals, involving the people who know the work best, and investing in the right skills and governance, organizations can:
- Streamline operations and reduce manual effort.
- Improve accuracy, compliance, and decision quality.
- Deliver faster, more responsive customer experiences.
- Free employees to focus on higher-value, more fulfilling work.
The opportunity is not just to do the same work faster, but to reimagine what your organization can achieve when digital workers and human workers collaborate by design. Thoughtfully deployed, RPA and AI become a sustained source of competitive advantage and a catalyst for continuous innovation.
